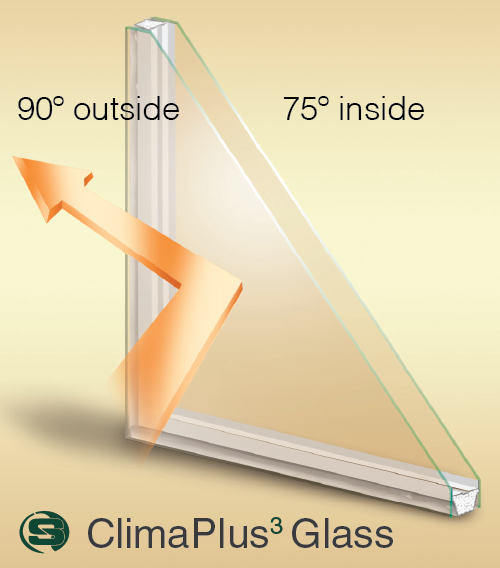
What is
Low-E Glass?
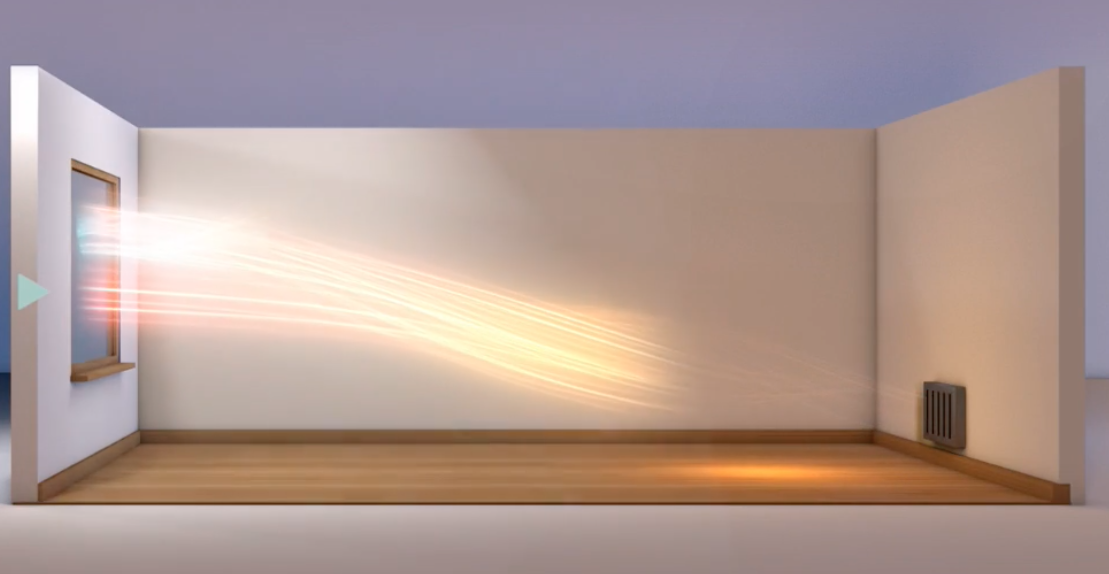
What is Low-E Glass? (low-emissivity) glass is a type of energy-efficient window glass that is coated with a thin layer of metallic oxide. This coating helps to reduce the amount of heat that is transmitted through the glass, which makes it more effective at keeping heat inside a building during the winter and outside during the summer. Low-e glass can also help to reduce the amount of ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation that passes through the window, which can help to protect furniture, flooring, and other household items from fading or damage. In addition to its energy-saving properties, low-e glass is also highly reflective, which can help to reduce glare and improve visibility.
Low-e glass has been around for several decades, and it has undergone many technological advances over the years. Some of the most significant improvements include:
- Improved coatings: The coatings used on low-e glass have become more advanced and effective over time. Modern low-e coatings are much thinner and more transparent than earlier versions, which makes them less noticeable and more aesthetically pleasing.
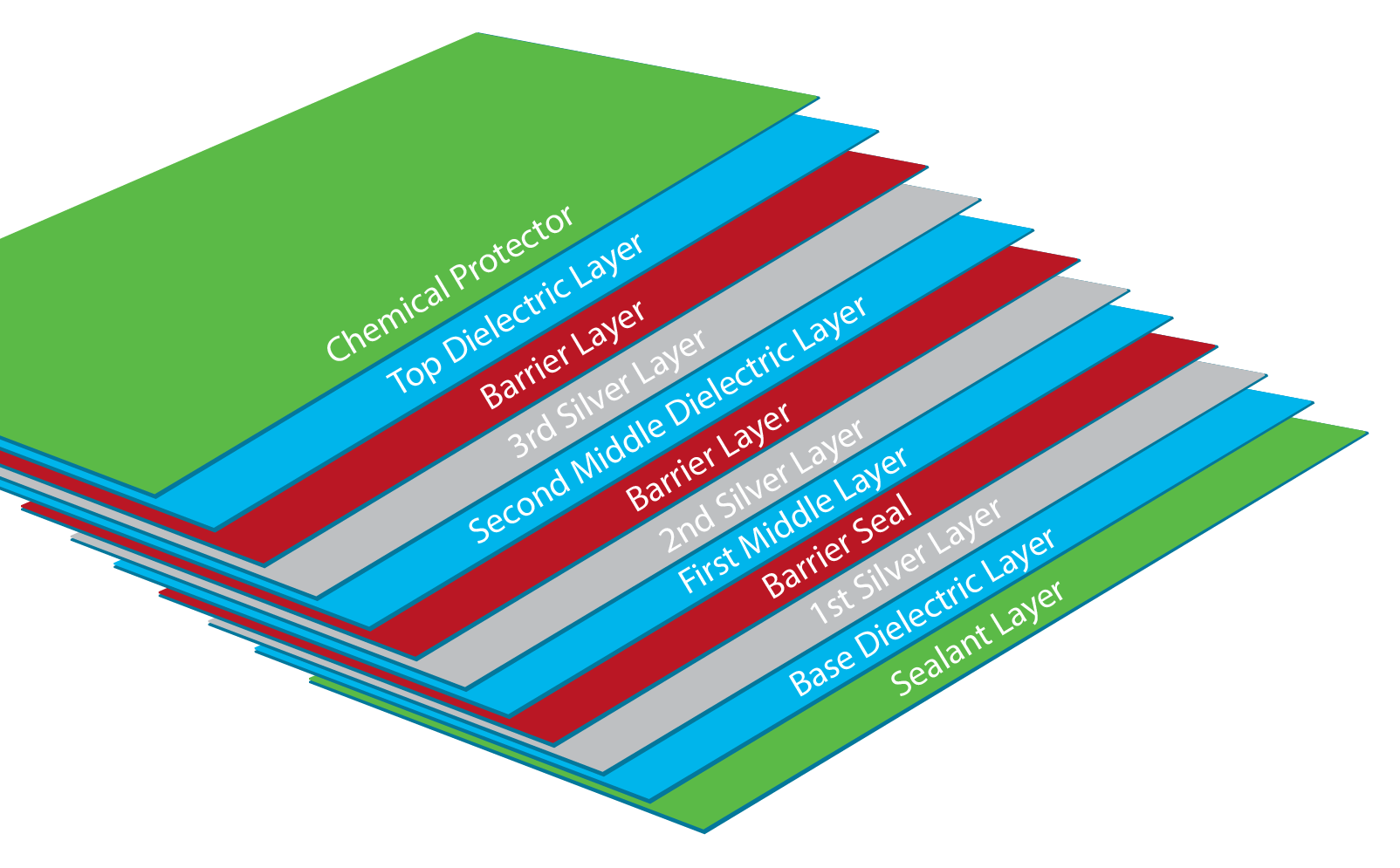
- Multiple layers: Some low-e glass products now use multiple layers of coatings to improve their energy-saving capabilities. These multilayer coatings can be customized to suit the specific needs of a building or climate.
- Improved energy performance: Low-e glass has become much more effective at saving energy over the years. In addition to reducing heat transmission, it can also reduce the amount of solar heat gain that enters a building, which can help to reduce the need for air conditioning.
Low-e glass, also known as low-emissivity glass, is a type of energy-efficient window that has been coated with a thin layer of metallic oxide. This special coating helps to reduce the amount of heat that is transmitted through the glass, making it more effective at keeping heat inside a building during the winter and outside during the summer. As a result, low-e glass can help to reduce energy consumption and lower energy bills. In addition to its energy-saving properties, low-e glass is also highly reflective, which can help to reduce glare and improve visibility.
There are several different types of low-e coatings available on the market, each with its own unique set of properties. Some low-e coatings are designed to reflect long-wave infrared radiation, which helps to keep heat inside a building. Others are designed to reflect short-wave infrared radiation, which helps to keep heat out. Still others are designed to reflect both long-wave and short-wave infrared radiation, providing a balance of both.
One of the primary benefits of low-e glass is its ability to improve a building’s energy efficiency. By reducing the amount of heat that is transmitted through the windows, low-e glass can help to keep a building warmer in the winter and cooler in the summer. This can significantly reduce the amount of energy that is needed to heat and cool a building, which can translate into lower energy bills. In addition, low-e glass can also help to reduce the amount of ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation that passes through the window, which can help to protect furniture, flooring, and other household items from fading or damage.
Low-e glass is also highly reflective, which can be beneficial in a number of ways. For one, it can help to reduce glare, making it easier to see through the windows. This can be especially helpful in areas with strong sunlight or in buildings with large windows. In addition, the reflective properties of low-e glass can help to improve the overall appearance of a building by adding a touch of shine and sparkle.
There are a few different factors to consider when choosing low-e glass for a building. One of the most important is the climate in which the building is located. In cold climates, it is generally best to choose a low-e coating that reflects long-wave infrared radiation, as this will help to keep the building warmer. In hot climates, on the other hand, a low-e coating that reflects short-wave infrared radiation is generally a better choice, as it will help to keep the building cooler.
Another factor to consider is the type of window frame that will be used. Some window frames are more energy-efficient than others, and choosing a high-quality frame can help to improve the overall energy efficiency of the window. Finally, it is also important to consider the size and orientation of the window, as well as the type of glass that will be used. All of these factors can affect the overall energy efficiency of the window.
In conclusion, low-e glass is a highly effective and energy-efficient option for windows. Its ability to reduce the amount of heat that is transmitted through the glass, as well as its reflective properties, make it a popular choice for both residential and commercial buildings. By choosing low-e glass, it is possible to improve the energy efficiency of a building, reduce energy costs, and protect furniture and other household items from fading or damage.



